Introduction
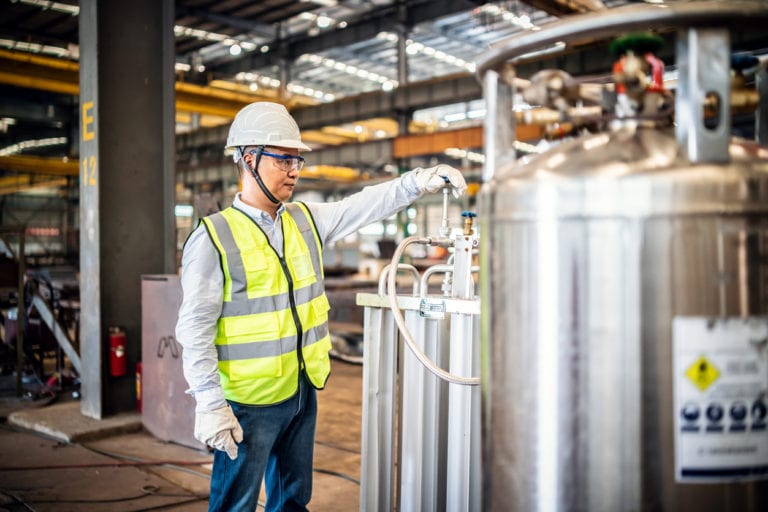
In hazardous industries, the presence of toxic and flammable gases is a significant concern. Ensuring the safety of workers and maintaining operational integrity relies heavily on the precise measurement and monitoring of these dangerous gases. This blog post explores the critical role of gas detection in hazardous industries, the common types of toxic and flammable gases encountered, and the advanced technologies used to measure them.
Importance of Gas Detection in Hazardous Industries
Protecting Worker Health and Safety
Worker safety is the top priority in hazardous environments. Toxic gases can cause serious health issues, including respiratory problems and poisoning, while flammable gases can lead to fires and explosions. Reliable gas detection systems provide early warnings, allowing for immediate action to prevent accidents and protect workers.
Regulatory Compliance
In the United States, industries must adhere to strict regulations set by agencies like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). These regulations mandate the continuous monitoring and reporting of gas levels to ensure a safe working environment. Implementing robust gas detection systems helps industries comply with these regulations, avoiding penalties and legal issues.
Environmental Protection
Gas leaks can have severe environmental impacts, contributing to air pollution and climate change. Effective gas detection helps industries minimize their environmental footprint by identifying leaks early and allowing for prompt corrective actions.
Safeguarding Assets and Infrastructure
Gas leaks can lead to catastrophic incidents, causing damage to equipment and infrastructure. Continuous gas monitoring helps detect leaks early, preventing costly repairs and operational downtime.
Common Toxic and Flammable Gases in Hazardous Industries
Toxic Gases
- Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): Commonly found in the oil and gas industry, hydrogen sulfide is highly toxic and poses severe health risks.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Produced by incomplete combustion, carbon monoxide is colorless, odorless, and highly poisonous.
- Ammonia (NH3): Used in various industrial processes, ammonia is toxic and can cause respiratory issues.
Flammable Gases
- Methane (CH4): Widely present in the oil and gas sector, methane is highly flammable and can lead to explosions.
- Propane (C3H8) and Butane (C4H10): Used as fuel sources, these gases are highly combustible and require careful handling.
- Hydrogen (H2): Used in refining and chemical processes, hydrogen is extremely flammable and poses significant explosion risks.
Cutting-Edge Gas Detection Technologies
Stationary Gas Detection Systems
Stationary gas detectors are permanently installed at strategic locations within industrial facilities to provide continuous monitoring of gas levels. These systems are connected to alarm and control mechanisms, ensuring immediate response when hazardous levels are detected, thereby enhancing safety and reducing risks.
Mobile Gas Detectors
Mobile gas detectors offer flexibility, enabling workers to measure gas levels in various areas. These portable devices are crucial for spot checks, confined space entries, and locations not covered by stationary detectors, ensuring comprehensive gas monitoring.
Wireless Gas Monitoring Systems
Wireless gas monitoring systems leverage advanced technology for real-time data transmission and monitoring. Ideal for large, complex facilities, these systems eliminate the need for extensive wiring, offering a practical solution for areas where traditional wired systems are impractical.
Integration with IoT and AI
Integrating gas detection systems with IoT and AI technologies significantly enhances safety protocols. IoT-enabled detectors continuously feed data to central monitoring systems, while AI algorithms analyze this data to predict potential leaks and suggest preventive measures, improving overall safety and efficiency.
Best Practices for Gas Detection in Hazardous Industries
Conduct Thorough Risk Assessments
Identify potential gas hazards and determine the appropriate detection technologies. Assess the types of gases present, their concentrations, and the specific areas of the facility that require monitoring.
Regular Maintenance and Calibration
Ensure that gas detection systems are regularly maintained and calibrated according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Regular maintenance ensures the accuracy and reliability of the detectors, preventing false alarms and ensuring prompt detection of actual leaks.
Provide Comprehensive Training
Educate workers on the use and importance of gas detection systems. Workers should be aware of the potential gas hazards, how to respond to alarms, and the proper use of portable gas detectors.
Develop Robust Emergency Response Plans
Create and implement comprehensive emergency response plans. These plans should include procedures for gas leak detection, evacuation, and communication protocols to ensure a swift and effective response.
Conclusion
In hazardous industries, measuring and monitoring toxic and flammable gases is critical for ensuring worker safety, regulatory compliance, and environmental protection. By leveraging advanced gas detection technologies and adhering to best practices, industries can mitigate risks, protect their workforce, and maintain operational integrity. Continuous advancements in gas detection, including the integration of IoT and AI, promise to further enhance safety and efficiency in these high-risk environments.
Contact our team of experts today to ensure you get the exact level of protection tailored to your specific job conditions.